【背景】
折腾:
期间,需要去实现,动态创建多个TAB页面。
【折腾过程】
1.google搜:
android dynamic create tab
然后参考:
TabView (Part4) – Create dynamic content in tab at run time | Android Tech
看到其用到TabHost,所以去查查。
2.参考:
新浪微博布局学习——妙用TabHost – 农民伯伯 – 博客园
Android TabHost的使用 – hpoi的专栏 – 博客频道 – CSDN.NET
最全的Android的Tab与TabHost讲解 – Android实例教程 – Android开发论坛 – 安卓开发论坛 – Android开发 – 安卓论坛 – 移动互联网门户
但是是用xml去定义固定的tab的。不是我要的。
3.关于动态创建Tab的,找到:
[1/2] Android学习笔记之——TabHost动态增加与删除与更新 | K-Beta
示例代码是:
1 | tabhost.addTab(tabhost.newTabSpec("tab" + j).setIndicator(mytabviewlist.get(j)) .setContent(Mytabfirst.this));//这里就是intent tabhost.setCurrentTab(j); |
但是还是没太大帮助。
4.算了,去参考:
去试试TabHost。
结果:
1 | tabHost = getTabHost(); |
中找不到getTabHost。
5.另外参考:
TabView (Part 1) – Simple tab control in Android | Android Tech
把概念解释的很清晰。去好好看看。
6.参考:
Android dynamic TAB Control « PocketMagic
去试试。
结果用代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 | // -- check screen orientation -- // m_display = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay(); m_nScreenW = m_display.getWidth(); m_nScreenH = m_display.getHeight(); // create interface View m_vForm; if (m_nScreenW <= m_nScreenH) m_vForm = _createTABForm(); // portrait interface else m_vForm = _createEmptyForm(); // landscape interface // show the panel on the screen setContentView(m_vForm); } /** Create the TAB interface */ @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") private ViewGroup _createTABForm() { // construct the TAB Host TabHost tabHost = new TabHost(this); tabHost.setLayoutParams( new LinearLayout.LayoutParams( LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT)); // the tabhost needs a tabwidget, that is a container for the visible tabs TabWidget tabWidget = new TabWidget(this); tabWidget.setId(android.R.id.tabs); tabHost.addView(tabWidget, new LinearLayout.LayoutParams( LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT)); // the tabhost needs a frame layout for the views associated with each visible tab FrameLayout frameLayout = new FrameLayout(this); frameLayout.setId(android.R.id.tabcontent); frameLayout.setPadding(0, 65, 0, 0); tabHost.addView(frameLayout, new LinearLayout.LayoutParams( LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); // setup must be called if you are not initialising the tabhost from XML tabHost.setup(); // create the tabs TabSpec ts1 = tabHost.newTabSpec("TAB_TAG_1"); ts1.setIndicator("TAB-1"); ts1.setContent(new TabHost.TabContentFactory(){ public View createTabContent(String tag) { // -- this tab contains multiple control grouped in a panel -- // LinearLayout panel = new LinearLayout(MainActivity.this); panel.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); panel.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL); // Userid : label and text field TextView lblUserid = new TextView(MainActivity.this); lblUserid.setText("The label above the EditText"); lblUserid.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, 10f); lblUserid.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); EditText ttfUserid = new EditText(MainActivity.this); ttfUserid.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); // login button final Button btnLogin = new Button(MainActivity.this); btnLogin.setText("Login"); btnLogin.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); btnLogin.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER); btnLogin.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View view) { Log.d("pocketmagic.net", "_createForm click but"); } }); // actually adding the views to the panel // userid panel.addView(lblUserid); panel.addView(ttfUserid); // loginbutton panel.addView(btnLogin); return panel; } //TAB 1 done }); tabHost.addTab(ts1);// // TabSpec ts2 = tabHost.newTabSpec("TAB_TAG_2");// ts2.setIndicator("TAB-2");// ts2.setContent(new TabHost.TabContentFactory(){// public View createTabContent(String tag)// {// // -- this tab contains a single control - the listview -- //// ListView ls1 = new ListView(MainActivity.this); // ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(// MainActivity.this,// android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,// new String[]{"item1","item2","item3","item4","item5","item6","item7"});// ls1.setAdapter(adapter); // ls1.setOnCreateContextMenuListener(MainActivity.this);// return ls1;// } // }); // tabHost.addTab(ts2);//// TabSpec ts3 = tabHost.newTabSpec("TAB_TAG_3");// ts3.setIndicator(" "); // ts3.setContent(new TabHost.TabContentFactory(){// public View createTabContent(String tag)// { // // -- this tab contains a single control - a textview -- //// TextView textAbout = new TextView(MainActivity.this);// textAbout.setText("About this sample\n\nThis is the Dynamic TAB control sample for Android.\n\n(C)2010 Radu Motisan\nradu.motisan@gmail.com\nwww.pocketmagic.net");// textAbout.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, 12f);// textAbout.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); // return textAbout;// } // }); // tabHost.addTab(ts3);// // -- set the image for tab3, can be used after tab has been created too -- //// ImageView iv = (ImageView)tabHost.getTabWidget().getChildAt(2).findViewById(android.R.id.icon);// if (iv != null) iv.setImageDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.icon)); return tabHost; } /** Create the empty interface for landscape*/ private View _createEmptyForm() { TextView text = new TextView(this); text.setText("The interface is only available in PORTRAIT mode! Do the switch :-)"); text.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, 18f); text.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); return text; } |
却挂掉了。
7.
这里:
解释了静态的TAB和动态的TAB的逻辑:
tab组件是:TabWidget
(1)静态使用tab:
用xml定义好对应的布局
创建一个TabHost.TabSpec
然后再调用setContent()
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 | TabHost.TabSpec spec=tabs.newTabSpec(“buttontab”);spec.setContent(R.id.buttontab);spec.setIndicator(“Button”);tabs.addTab(spec); |
(2)动态使用tab:
和静态的很类似:
唯一不同的只是
setContent()
时传入的是的TabHost.TabContentFactory实例
提供一个对应的createTabContent()的callback,返回view即可。
8.官网:
没有解释清楚,如何去动态的添加tab。
9.再去看:
TabWidget | Android Developers
还是没思路。
10.最后还是参考:
TabView (Part 1) – Simple tab control in Android | Android Tech
而用如下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | import android.widget.TabHost;import android.widget.TabHost.TabSpec;public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); TabHost tabHost=(TabHost)findViewById(R.id.tabHost); tabHost.setup(); TabSpec spec1=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab 1"); spec1.setContent(R.id.tab1); spec1.setIndicator("Tab 1"); TabSpec spec2=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab 2"); spec2.setIndicator("Tab 2"); spec2.setContent(R.id.tab2); TabSpec spec3=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab 3"); spec3.setIndicator("Tab 3"); spec3.setContent(R.id.tab3); tabHost.addTab(spec1); tabHost.addTab(spec2); tabHost.addTab(spec3); } |
对应xml是:
/res/layout/activity_main.xml
内容为:
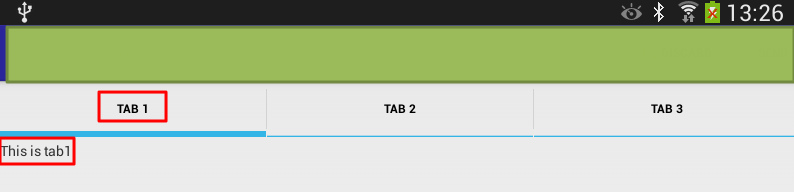
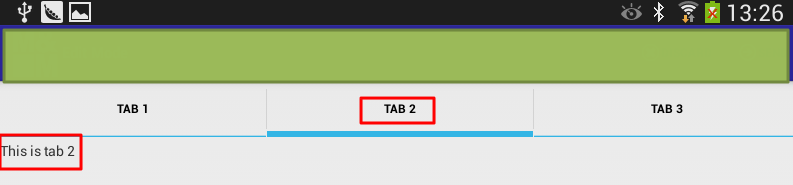
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><TabHost android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/tabHost" <TabWidget android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@android:id/tabs"/> <FrameLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/tab1" android:orientation="vertical" android:paddingTop="60px"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="100px" android:text="This is tab1" android:id="@+id/txt1"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/tab2" android:orientation="vertical" android:paddingTop="60px"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="100px" android:text="This is tab 2" android:id="@+id/txt2"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/tab3" android:orientation="vertical" android:paddingTop="60px"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="100px" android:text="This is tab 3" android:id="@+id/txt3"/> </LinearLayout> </FrameLayout></TabHost> |
然后可以显示出对应的三个TAB了:
11.然后再继续参考教程:
TabView (Part4) – Create dynamic content in tab at run time | Android Tech
去改为动态添加tab:
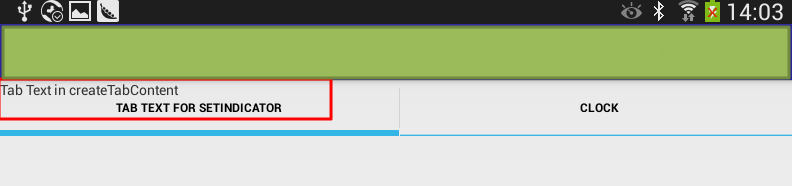
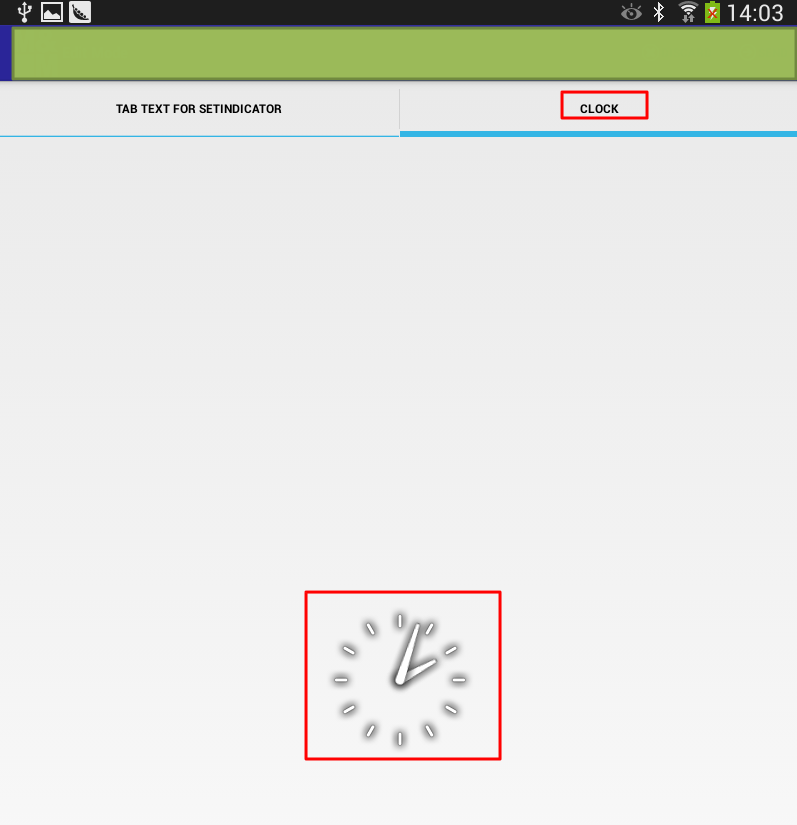
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | TabHost tabHost=(TabHost)findViewById(R.id.tabHost);tabHost.setup();TabSpec spec1=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1");spec1.setContent(new TabHost.TabContentFactory() { public View createTabContent(String tag) { TextView txtView = new TextView(MainActivity.this); txtView.setText("Tab Text in createTabContent"); return txtView; }});spec1.setIndicator("Tab Text for setIndicator");TabSpec spec2=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab2");spec2.setIndicator("Tab Clock");spec2.setContent(new TabHost.TabContentFactory() { public View createTabContent(String tag) { return(new AnalogClock(MainActivity.this)); }});spec2.setIndicator("Clock");tabHost.addTab(spec1);tabHost.addTab(spec2); |
效果如下:
【总结】
此处,很明显是第一个tab添加后,text显示位置有误,但是暂时不去深究。
总之对于动态添加tab的功能,是实现了。
总结如下:
去
/res/layout/activity_main.xml
建立对应的布局配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><TabHost android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@+id/tabHost" <TabWidget android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@android:id/tabs"/> <FrameLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"> </FrameLayout></TabHost> |
然后去代码中,动态添加tab:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | import android.view.Menu;import android.view.View;import android.widget.AnalogClock;import android.widget.TabHost;import android.widget.TabHost.TabSpec;import android.widget.TextView;public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); TabHost tabHost=(TabHost)findViewById(R.id.tabHost); tabHost.setup(); TabSpec spec1=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1"); spec1.setContent(new TabHost.TabContentFactory() { public View createTabContent(String tag) { TextView txtView = new TextView(MainActivity.this); txtView.setText("Tab Text in createTabContent"); return txtView; } }); spec1.setIndicator("Tab Text for setIndicator"); TabSpec spec2=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab2"); spec2.setIndicator("Tab Clock"); spec2.setContent(new TabHost.TabContentFactory() { public View createTabContent(String tag) { return(new AnalogClock(MainActivity.this)); } }); spec2.setIndicator("Clock"); tabHost.addTab(spec1); tabHost.addTab(spec2); } |
即可。
转载请注明:在路上 » 【已解决】Android中动态创建多个TAB页面