【背景】
折腾:
【记录】尝试用QEMU模拟ARM开发板去加载并运行Uboot,kernel,rootfs
期间,准备好了之后,去调用QEMU启动内核。
【折腾过程】
1.启动内核,结果出错,折腾半天,终于运行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 | crifan@ubuntu:etc$ sudo qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootsudo: qemu-system-arm: command not foundcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: could not configure /dev/net/tun (tap0): Operation not permittedqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: Device 'tap' could not be initializedcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ envSSH_AGENT_PID=1775GPG_AGENT_INFO=/run/user/crifan/keyring-FO1RtG/gpg:0:1SHELL=/bin/bashTERM=xtermXDG_SESSION_COOKIE=0a0bee208665f2e846489a7a5201cc2e-1376644437.803328-1757185WINDOWID=52428806GNOME_KEYRING_CONTROL=/run/user/crifan/keyring-FO1RtGOLDPWD=/home/crifan/develop/embedded/qemu/ifup_ifdownGTK_MODULES=overlay-scrollbarUSER=crifanLS_COLORS=rs=0:di=01;34:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.Z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.tbz2=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.war=01;31:*.ear=01;31:*.sar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpio=01;31:*.7z=01;31:*.rz=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.webm=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=01;35:*.axv=01;35:*.anx=01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=00;36:*.au=00;36:*.flac=00;36:*.mid=00;36:*.midi=00;36:*.mka=00;36:*.mp3=00;36:*.mpc=00;36:*.ogg=00;36:*.ra=00;36:*.wav=00;36:*.axa=00;36:*.oga=00;36:*.spx=00;36:*.xspf=00;36:XDG_SESSION_PATH=/org/freedesktop/DisplayManager/Session0XDG_SEAT_PATH=/org/freedesktop/DisplayManager/Seat0SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/run/user/crifan/keyring-FO1RtG/sshSESSION_MANAGER=local/ubuntu:@/tmp/.ICE-unix/1724,unix/ubuntu:/tmp/.ICE-unix/1724DEFAULTS_PATH=/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.default.pathXDG_CONFIG_DIRS=/etc/xdg/xdg-ubuntu:/etc/xdgPATH=/usr/lib/lightdm/lightdm:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/crosstool-ng/bin:/opt/crosscompile/xscale/gcc-4.6.0-glibc-2.9/bin:/opt/crosscompile/curl/bin:/opt/crosscompile/pcre/bin:/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.7.0-openjdk-i386/:/opt/qemu/binDESKTOP_SESSION=ubuntuPWD=/etcLANG=en_US.UTF-8MANDATORY_PATH=/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.mandatory.pathUBUNTU_MENUPROXY=libappmenu.soCOMPIZ_CONFIG_PROFILE=ubuntuGDMSESSION=ubuntuSHLVL=1HOME=/home/crifanGNOME_DESKTOP_SESSION_ID=this-is-deprecatedLOGNAME=crifanXDG_DATA_DIRS=/usr/share/ubuntu:/usr/share/gnome:/usr/local/share/:/usr/share/DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-X61uGuuYXI,guid=1f0c8b206525a43143fa5369520ded56LESSOPEN=| /usr/bin/lesspipe %sTEXTDOMAIN=im-configDISPLAY=:0.0XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/crifanXDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP=UnityLESSCLOSE=/usr/bin/lesspipe %s %sTEXTDOMAINDIR=/usr/share/locale/XAUTHORITY=/home/crifan/.XauthorityCOLORTERM=gnome-terminal_=/usr/bin/envcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ ls /opt/qemu/binqemu-arm qemu-ga qemu-img qemu-io qemu-nbd qemu-system-armcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ ls /opt/qemu/bin -lhatotal 27Mdrwxr-xr-x 2 crifan crifan 4.0K Aug 15 03:24 .drwxr-xr-x 7 crifan crifan 4.0K Aug 15 02:51 ..-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan crifan 3.2M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-arm-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan crifan 778K Aug 15 03:24 qemu-ga-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan crifan 2.0M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-img-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan crifan 2.0M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-io-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan crifan 1.9M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-nbd-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan crifan 17M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-system-armcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ sudo qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootsudo: qemu-system-arm: command not foundcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: could not configure /dev/net/tun (tap0): Operation not permittedqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: Device 'tap' could not be initializedcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ chown crifan /dev/net/tunchown: changing ownership of ‘/dev/net/tun’: Operation not permittedcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ sudo chown crifan /dev/net/tuncrifan@ubuntu:etc$ ls /dev/net/ -lhatotal 0drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 60 Aug 16 02:13 .drwxr-xr-x 15 root root 4.3K Aug 16 02:13 ..crw-rw-rwT 1 crifan root 10, 200 Aug 16 02:13 tuncrifan@ubuntu:etc$ qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: could not configure /dev/net/tun (tap0): Operation not permittedqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: Device 'tap' could not be initializedcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ sudo qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootsudo: qemu-system-arm: command not foundcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ chgrp --helpUsage: chgrp [OPTION]... GROUP FILE... or: chgrp [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...Change the group of each FILE to GROUP.With --reference, change the group of each FILE to that of RFILE. -c, --changes like verbose but report only when a change is made -f, --silent, --quiet suppress most error messages -v, --verbose output a diagnostic for every file processed --dereference affect the referent of each symbolic link (this is the default), rather than the symbolic link itself -h, --no-dereference affect symbolic links instead of any referenced file (useful only on systems that can change the ownership of a symlink) --no-preserve-root do not treat '/' specially (the default) --preserve-root fail to operate recursively on '/' --reference=RFILE use RFILE's group rather than specifying a GROUP value -R, --recursive operate on files and directories recursivelyThe following options modify how a hierarchy is traversed when the -Roption is also specified. If more than one is specified, only the finalone takes effect. -H if a command line argument is a symbolic link to a directory, traverse it -L traverse every symbolic link to a directory encountered -P do not traverse any symbolic links (default) --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exitExamples: chgrp staff /u Change the group of /u to "staff". chgrp -hR staff /u Change the group of /u and subfiles to "staff".Report chgrp bugs to bug-coreutils@gnu.orgGNU coreutils home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'chgrp invocation'crifan@ubuntu:etc$ chgrp -R root /opt/qemu/crifan@ubuntu:etc$ sudo qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootsudo: qemu-system-arm: command not foundcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-bootqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: could not configure /dev/net/tun (tap0): Operation not permittedqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: Device 'tap' could not be initializedcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ qemu-qemu-arm qemu-ga qemu-img qemu-io qemu-nbd qemu-system-arm crifan@ubuntu:etc$ qemu-system-arm ^Ccrifan@ubuntu:etc$ ls /opt/qemu/ -lhatotal 28Kdrwxr-xr-x 7 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 02:51 .drwxr-xr-x 7 crifan root 4.0K Aug 16 01:40 ..drwxr-xr-x 2 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 03:24 bindrwxr-xr-x 3 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 02:51 etcdrwxr-xr-x 2 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 03:24 libexecdrwxr-xr-x 5 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 02:51 sharedrwxr-xr-x 3 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 02:51 varcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ ls /opt/qemu/bin -lhatotal 27Mdrwxr-xr-x 2 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 03:24 .drwxr-xr-x 7 crifan root 4.0K Aug 15 02:51 ..-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan root 3.2M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-arm-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan root 778K Aug 15 03:24 qemu-ga-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan root 2.0M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-img-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan root 2.0M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-io-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan root 1.9M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-nbd-rwxr-xr-x 1 crifan root 17M Aug 15 03:24 qemu-system-armcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ sudo /opt/qemu/bin/qemu-system-arm -M versatilepb -nographic -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0 -kernel /home/crifan/develop/crosscompile/uboot/u-boot-2013.07/u-boot/sbin/ifdown: interface eth0 not configured/etc/qemu-ifup: 19: /etc/qemu-ifup: /usr/sbin/openvpn: not found/etc/qemu-ifup: 24: /etc/qemu-ifup: /usr/sbin/brctl: not found/etc/qemu-ifup: 25: /etc/qemu-ifup: /usr/sbin/brctl: not found/etc/qemu-ifup: 26: /etc/qemu-ifup: /usr/sbin/brctl: not found/etc/qemu-ifup: 30: /etc/qemu-ifup: /usr/sbin/brctl: not foundSIOCSIFADDR: No such devicebr0: ERROR while getting interface flags: No such deviceSIOCSIFNETMASK: No such deviceSIOCSIFBRDADDR: No such devicebr0: ERROR while getting interface flags: No such deviceSIOCADDRT: Network is unreachable/etc/qemu-ifup: 39: /etc/qemu-ifup: /sbin/service: not found/etc/qemu-ifup: could not launch network scriptqemu-system-arm: -net tap,ifname=tap0: Device 'tap' could not be initializedcrifan@ubuntu:etc$ |
2.关于网络问题,折腾过程见:
【已解决】Ubuntu下QEMU启动内核时出错:/etc/qemu-ifup: 19: /etc/qemu-ifup: /usr/sbin/openvpn: not found
和
【未解决】Ubuntu下用QEMU启动内核时出错:SIOCSIFADDR: No such device
注:
这个帖子,有空可以看看:
3.但是很明显,对于另外,由于之前看到别的教程,觉得更合适,所以打算先去参考那个帖子:
Compiling Linux kernel for QEMU ARM emulator
去折腾完,再回来弄此处的网络。
4.后来发现有新帖子:
Compile Linux kernel 3.2 for ARM and emulate with QEMU
参考新帖子,去试试:
5.关于initramfs,顺带去看了看对应的文档:
1 2 3 4 5 | is readycrifan@ubuntu:linux-3.10.7$ gedit Documentation/eearly-userspace/ edac.txt eisa.txt email-clients.txt extcon/ crifan@ubuntu:linux-3.10.7$ gedit Documentation/early-userspace/buffer-format.txt README |
内容为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 | Early userspace support=======================Last update: 2004-12-20 tlh"Early userspace" is a set of libraries and programs that providevarious pieces of functionality that are important enough to beavailable while a Linux kernel is coming up, but that don't need to berun inside the kernel itself.It consists of several major infrastructure components:- gen_init_cpio, a program that builds a cpio-format archive containing a root filesystem image. This archive is compressed, and the compressed image is linked into the kernel image.- initramfs, a chunk of code that unpacks the compressed cpio image midway through the kernel boot process.- klibc, a userspace C library, currently packaged separately, that is optimized for correctness and small size.The cpio file format used by initramfs is the "newc" (aka "cpio -H newc")format, and is documented in the file "buffer-format.txt". There aretwo ways to add an early userspace image: specify an existing cpioarchive to be used as the image or have the kernel build process buildthe image from specifications.CPIO ARCHIVE methodYou can create a cpio archive that contains the early userspace image.Your cpio archive should be specified in CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE and itwill be used directly. Only a single cpio file may be specified inCONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE and directory and file names are not allowed incombination with a cpio archive.IMAGE BUILDING methodThe kernel build process can also build an early userspace image fromsource parts rather than supplying a cpio archive. This method providesa way to create images with root-owned files even though the image wasbuilt by an unprivileged user.The image is specified as one or more sources inCONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE. Sources can be either directories or files -cpio archives are *not* allowed when building from sources.A source directory will have it and all of its contents packaged. Thespecified directory name will be mapped to '/'. When packaging adirectory, limited user and group ID translation can be performed.INITRAMFS_ROOT_UID can be set to a user ID that needs to be mapped touser root (0). INITRAMFS_ROOT_GID can be set to a group ID that needsto be mapped to group root (0).A source file must be directives in the format required by theusr/gen_init_cpio utility (run 'usr/gen_init_cpio --help' to get thefile format). The directives in the file will be passed directly tousr/gen_init_cpio.When a combination of directories and files are specified then theinitramfs image will be an aggregate of all of them. In this way a usercan create a 'root-image' directory and install all files into it.Because device-special files cannot be created by a unprivileged user,special files can be listed in a 'root-files' file. Both 'root-image'and 'root-files' can be listed in CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE and a completeearly userspace image can be built by an unprivileged user.As a technical note, when directories and files are specified, theentire CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCE is passed toscripts/gen_initramfs_list.sh. This means that CONFIG_INITRAMFS_SOURCEcan really be interpreted as any legal argument togen_initramfs_list.sh. If a directory is specified as an argument thenthe contents are scanned, uid/gid translation is performed, andusr/gen_init_cpio file directives are output. If a directory isspecified as an arugemnt to scripts/gen_initramfs_list.sh then thecontents of the file are simply copied to the output. All of the outputdirectives from directory scanning and file contents copying areprocessed by usr/gen_init_cpio.See also 'scripts/gen_initramfs_list.sh -h'.Where's this all leading?=========================The klibc distribution contains some of the necessary software to makeearly userspace useful. The klibc distribution is currentlymaintained separately from the kernel, but this may change early inthe 2.7 era (it missed the boat for 2.5).You can obtain somewhat infrequent snapshots of klibc fromftp://ftp.kernel.org/pub/linux/libs/klibc/For active users, you are better off using the klibc gitrepository, at http://git.kernel.org/?p=libs/klibc/klibc.gitThe standalone klibc distribution currently provides three components,in addition to the klibc library:- ipconfig, a program that configures network interfaces. It can configure them statically, or use DHCP to obtain information dynamically (aka "IP autoconfiguration").- nfsmount, a program that can mount an NFS filesystem.- kinit, the "glue" that uses ipconfig and nfsmount to replace the old support for IP autoconfig, mount a filesystem over NFS, and continue system boot using that filesystem as root.kinit is built as a single statically linked binary to save space.Eventually, several more chunks of kernel functionality will hopefullymove to early userspace:- Almost all of init/do_mounts* (the beginning of this is already in place)- ACPI table parsing- Insert unwieldy subsystem that doesn't really need to be in kernel space hereIf kinit doesn't meet your current needs and you've got bytes to burn,the klibc distribution includes a small Bourne-compatible shell (ash)and a number of other utilities, so you can replace kinit and buildcustom initramfs images that meet your needs exactly.For questions and help, you can sign up for the early userspacemailing list at http://www.zytor.com/mailman/listinfo/klibcHow does it work?=================The kernel has currently 3 ways to mount the root filesystem:a) all required device and filesystem drivers compiled into the kernel, no initrd. init/main.c:init() will call prepare_namespace() to mount the final root filesystem, based on the root= option and optional init= to run some other init binary than listed at the end of init/main.c:init().b) some device and filesystem drivers built as modules and stored in an initrd. The initrd must contain a binary '/linuxrc' which is supposed to load these driver modules. It is also possible to mount the final root filesystem via linuxrc and use the pivot_root syscall. The initrd is mounted and executed via prepare_namespace().c) using initramfs. The call to prepare_namespace() must be skipped. This means that a binary must do all the work. Said binary can be stored into initramfs either via modifying usr/gen_init_cpio.c or via the new initrd format, an cpio archive. It must be called "/init". This binary is responsible to do all the things prepare_namespace() would do. To maintain backwards compatibility, the /init binary will only run if it comes via an initramfs cpio archive. If this is not the case, init/main.c:init() will run prepare_namespace() to mount the final root and exec one of the predefined init binaries.Bryan O'Sullivan <bos@serpentine.com> |
6.再去创建对应的init.c文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | #include <stdio.h> void main() { printf("Hello World!\n"); while(1);} |
然后去编译:
1 2 3 | crifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ arm-xscale-linux-gnueabi-gcc -static -o init init.ccrifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ file initinit: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, for GNU/Linux 2.6.19, not stripped |
7.先去看看cpio有哪些参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 | crifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ cpio --helpUsage: cpio [OPTION...] [destination-directory]GNU `cpio' copies files to and from archivesExamples: # Copy files named in name-list to the archive cpio -o < name-list [> archive] # Extract files from the archive cpio -i [< archive] # Copy files named in name-list to destination-directory cpio -p destination-directory < name-list Main operation mode: -i, --extract Extract files from an archive (run in copy-in mode) -o, --create Create the archive (run in copy-out mode) -p, --pass-through Run in copy-pass mode -t, --list Print a table of contents of the input Operation modifiers valid in any mode: --block-size=BLOCK-SIZE Set the I/O block size to BLOCK-SIZE * 512 bytes -B Set the I/O block size to 5120 bytes -c Use the old portable (ASCII) archive format -C, --io-size=NUMBER Set the I/O block size to the given NUMBER of bytes --force-local Archive file is local, even if its name contains colons -f, --nonmatching Only copy files that do not match any of the given patterns -F, --file=[[USER@]HOST:]FILE-NAME Use this FILE-NAME instead of standard input or output. Optional USER and HOST specify the user and host names in case of a remote archive -H, --format=FORMAT Use given archive FORMAT -M, --message=STRING Print STRING when the end of a volume of the backup media is reached -n, --numeric-uid-gid In the verbose table of contents listing, show numeric UID and GID --quiet Do not print the number of blocks copied --rsh-command=COMMAND Use remote COMMAND instead of rsh -v, --verbose Verbosely list the files processed -V, --dot Print a "." for each file processed -W, --warning=FLAG Control warning display. Currently FLAG is one of 'none', 'truncate', 'all'. Multiple options accumulate. Operation modifiers valid only in copy-in mode: -b, --swap Swap both halfwords of words and bytes of halfwords in the data. Equivalent to -sS -r, --rename Interactively rename files -s, --swap-bytes Swap the bytes of each halfword in the files -S, --swap-halfwords Swap the halfwords of each word (4 bytes) in the files --to-stdout Extract files to standard output -E, --pattern-file=FILE Read additional patterns specifying filenames to extract or list from FILE --only-verify-crc When reading a CRC format archive, only verify the CRC's of each file in the archive, don't actually extract the files Operation modifiers valid only in copy-out mode: -A, --append Append to an existing archive. -O [[USER@]HOST:]FILE-NAME Archive filename to use instead of standard output. Optional USER and HOST specify the user and host names in case of a remote archive Operation modifiers valid only in copy-pass mode: -l, --link Link files instead of copying them, when possible Operation modifiers valid in copy-in and copy-out modes: --absolute-filenames Do not strip file system prefix components from the file names --no-absolute-filenames Create all files relative to the current directory Operation modifiers valid in copy-out and copy-pass modes: -0, --null A list of filenames is terminated by a null character instead of a newline -a, --reset-access-time Reset the access times of files after reading them -I [[USER@]HOST:]FILE-NAME Archive filename to use instead of standard input. Optional USER and HOST specify the user and host names in case of a remote archive -L, --dereference Dereference symbolic links (copy the files that they point to instead of copying the links). -R, --owner=[USER][:.][GROUP] Set the ownership of all files created to the specified USER and/or GROUP Operation modifiers valid in copy-in and copy-pass modes: -d, --make-directories Create leading directories where needed -m, --preserve-modification-time Retain previous file modification times when creating files --no-preserve-owner Do not change the ownership of the files --sparse Write files with large blocks of zeros as sparse files -u, --unconditional Replace all files unconditionally -?, --help give this help list --usage give a short usage message --version print program versionMandatory or optional arguments to long options are also mandatory or optionalfor any corresponding short options.Report bugs to <bug-cpio@gnu.org>.crifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ which cpio/bin/cpiocrifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ |
再去用cpio弄出个initramfs:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | crifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ echo init | cpio -o -H newc > initramfs1123 blockscrifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ lsinit init.c initramfscrifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ ls -lhatotal 1.2Mdrwxrwxr-x 2 crifan crifan 4.0K Aug 18 22:54 .drwxrwxr-x 6 crifan crifan 4.0K Aug 18 22:50 ..-rwxrwxr-x 1 crifan crifan 561K Aug 18 22:51 init-rw-rw-r-- 1 crifan crifan 77 Aug 18 22:51 init.c-rw-rw-r-- 1 crifan crifan 562K Aug 18 22:54 initramfscrifan@ubuntu:rootfs$ |
8.然后去运行试试,结果是虽然可以调出QEMU窗口,但是运行出错,没有显示出我们要的hello world,而且出现了“Kernel Panic – Not syncing : Attempted to kill init !”的错误:
【已解决】QEMU运行kernel出错:Kernel Panic – Not syncing : Attempted to kill init
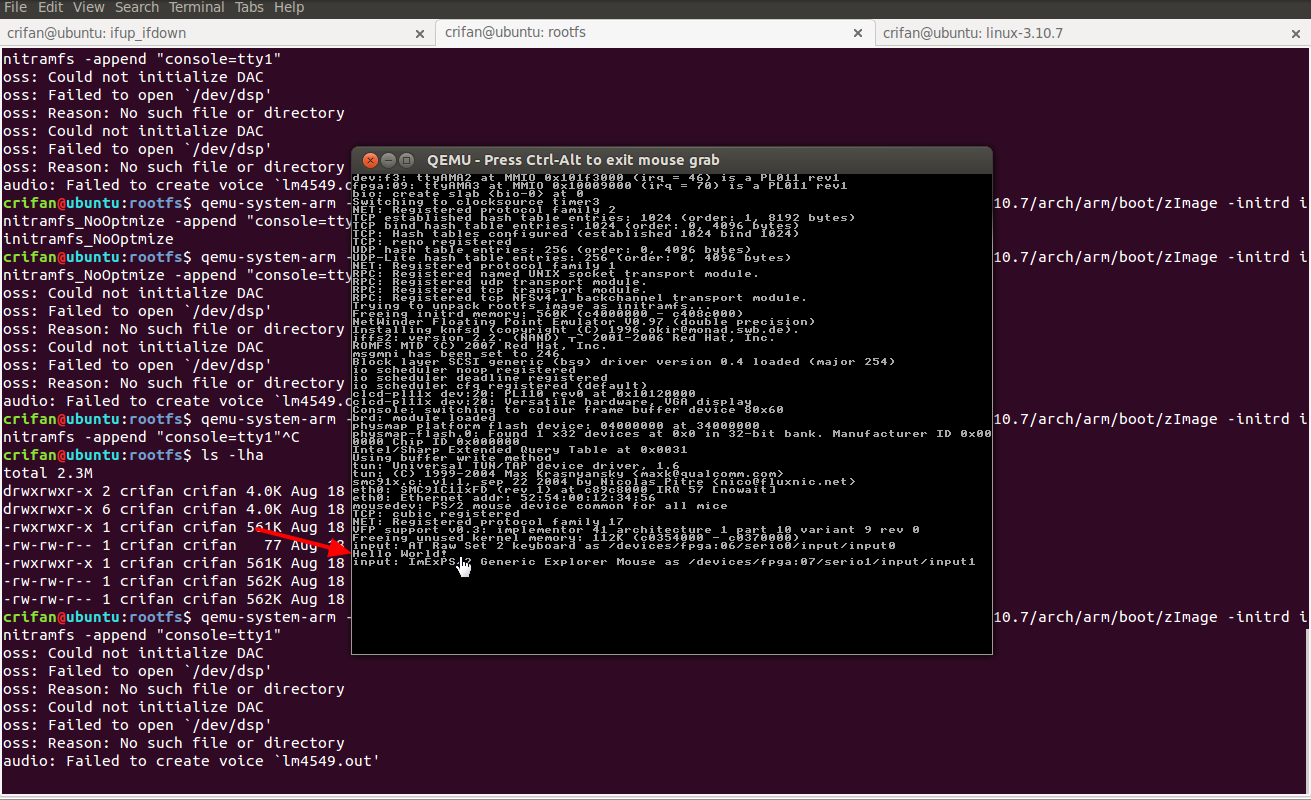
效果如图:
【总结】
至此,就可以正常运行kernel,并输出hello world了。
步骤和注意事项是:
1.重新编译内核,选上对应的EABI:
| Kernel Features -> [*] Use the ARM EABI to compile the kernel |
2.然后再去按照教程去操作,就可以输出hello world了。
转载请注明:在路上 » 【记录】Ubuntu下使用QEMU启动Linux内核