之前自己的gitbook的template的
make deploy
期间会用用了sshpass的rsync去通过ssh上传同步文件到自己的book.crifan.com中:
1 | sshpass -f /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/common/config/deploy/deploy_server_password.txt rsync -avzh --progress --stats --delete --force /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/generated/books/android_app_security_crack/release/android_app_security_crack root@149.28.136.189:/data/wwwroot/book.crifan.com/books |
但是往往速度很慢。
用了Trojan的全局代理
以及命令行用上代理设置:
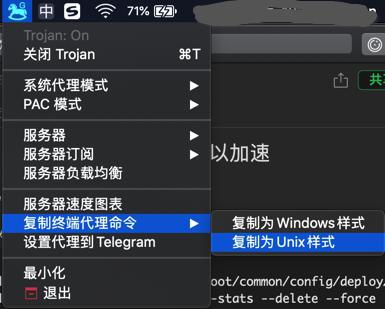
1 | export HTTP_PROXY=http://127.0.0.1:58591; export HTTPS_PROXY=http://127.0.0.1:58591; export ALL_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:51837 |
结果速度依旧很慢。
甚至最后超时了:
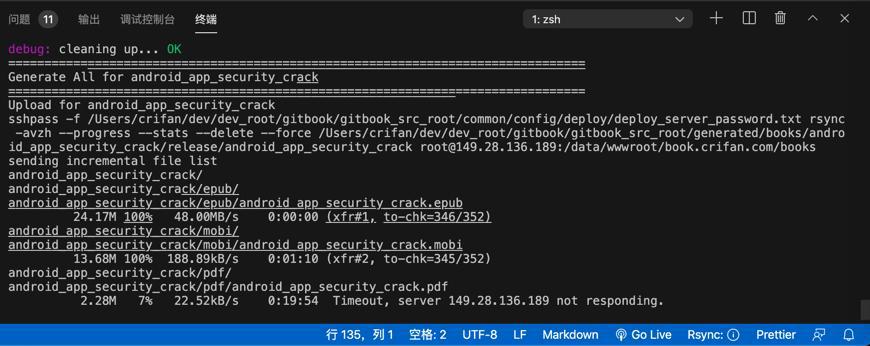
现象希望是:
在此处有代理可用的情况下,加上代理,以加速 提速
rsync 加速
rsync 加速 代理
去试试
不过试之前,去看看参数
1 2 3 4 | rsync -Pavzr-e "ssh -o 'ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:1080 %h %p' -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -o ServerAliveCountMax=20" //使用 ssh 做通讯,并使用 sock5 代理,代理地址:127.0.0.1 ,端口:1080root@192.168.0.100:/home/wwwroot/abc //from address/data/wwwroot/abc //to address |
的含义
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 | rsync --help rsync version 3.1.3 protocol version 31Copyright (C) 1996-2018 by Andrew Tridgell, Wayne Davison, and others.Web site: http://rsync.samba.org/Capabilities: 64-bit files, 64-bit inums, 64-bit timestamps, 64-bit long ints, socketpairs, hardlinks, symlinks, IPv6, batchfiles, inplace, append, ACLs, xattrs, iconv, symtimes, no prealloc, file-flagsrsync comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. This is free software, and youare welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. See the GNUGeneral Public Licence for details.rsync is a file transfer program capable of efficient remote updatevia a fast differencing algorithm.Usage: rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... DEST or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST:DEST or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST::DEST or rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/DEST or rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST:SRC [DEST] or rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST::SRC [DEST] or rsync [OPTION]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/SRC [DEST]to an rsync daemon, and require SRC or DEST to start with a module name.Options -v, --verbose increase verbosity --info=FLAGS fine-grained informational verbosity --debug=FLAGS fine-grained debug verbosity --msgs2stderr special output handling for debugging -q, --quiet suppress non-error messages --no-motd suppress daemon-mode MOTD (see manpage caveat) -c, --checksum skip based on checksum, not mod-time & size -a, --archive archive mode; equals -rlptgoD (no -H,-A,-X) --no-OPTION turn off an implied OPTION (e.g. --no-D) -r, --recursive recurse into directories -R, --relative use relative path names --no-implied-dirs don't send implied dirs with --relative -b, --backup make backups (see --suffix & --backup-dir) --backup-dir=DIR make backups into hierarchy based in DIR --suffix=SUFFIX set backup suffix (default ~ w/o --backup-dir) -u, --update skip files that are newer on the receiver --inplace update destination files in-place (SEE MAN PAGE) --append append data onto shorter files --append-verify like --append, but with old data in file checksum -d, --dirs transfer directories without recursing -l, --links copy symlinks as symlinks -L, --copy-links transform symlink into referent file/dir --copy-unsafe-links only "unsafe" symlinks are transformed --safe-links ignore symlinks that point outside the source tree --munge-links munge symlinks to make them safer (but unusable) -k, --copy-dirlinks transform symlink to a dir into referent dir -K, --keep-dirlinks treat symlinked dir on receiver as dir -H, --hard-links preserve hard links -p, --perms preserve permissions --fileflags preserve file-flags (aka chflags) -E, --executability preserve the file's executability --chmod=CHMOD affect file and/or directory permissions -A, --acls preserve ACLs (implies --perms) -X, --xattrs preserve extended attributes -o, --owner preserve owner (super-user only) -g, --group preserve group --devices preserve device files (super-user only) --specials preserve special files -D same as --devices --specials -t, --times preserve modification times -N, --crtimes preserve create times (newness) -O, --omit-dir-times omit directories from --times -J, --omit-link-times omit symlinks from --times --super receiver attempts super-user activities --fake-super store/recover privileged attrs using xattrs -S, --sparse turn sequences of nulls into sparse blocks --preallocate pre-allocate dest files on remote receiver -n, --dry-run perform a trial run with no changes made -W, --whole-file copy files whole (without delta-xfer algorithm) --checksum-choice=STR choose the checksum algorithms -x, --one-file-system don't cross filesystem boundaries -B, --block-size=SIZE force a fixed checksum block-size -e, --rsh=COMMAND specify the remote shell to use --rsync-path=PROGRAM specify the rsync to run on the remote machine --existing skip creating new files on receiver --ignore-existing skip updating files that already exist on receiver --remove-source-files sender removes synchronized files (non-dirs) --del an alias for --delete-during --delete delete extraneous files from destination dirs --delete-before receiver deletes before transfer, not during --delete-during receiver deletes during the transfer --delete-delay find deletions during, delete after --delete-after receiver deletes after transfer, not during --delete-excluded also delete excluded files from destination dirs --ignore-missing-args ignore missing source args without error --delete-missing-args delete missing source args from destination --ignore-errors delete even if there are I/O errors --force-delete force deletion of directories even if not empty --force-change affect user-/system-immutable files/dirs --force-uchange affect user-immutable files/dirs --force-schange affect system-immutable files/dirs --max-delete=NUM don't delete more than NUM files --max-size=SIZE don't transfer any file larger than SIZE --min-size=SIZE don't transfer any file smaller than SIZE --partial keep partially transferred files --partial-dir=DIR put a partially transferred file into DIR --delay-updates put all updated files into place at transfer's end -m, --prune-empty-dirs prune empty directory chains from the file-list --numeric-ids don't map uid/gid values by user/group name --usermap=STRING custom username mapping --groupmap=STRING custom groupname mapping --chown=USER:GROUP simple username/groupname mapping --timeout=SECONDS set I/O timeout in seconds --contimeout=SECONDS set daemon connection timeout in seconds -I, --ignore-times don't skip files that match in size and mod-time -M, --remote-option=OPTION send OPTION to the remote side only --size-only skip files that match in size -@, --modify-window=NUM set the accuracy for mod-time comparisons -T, --temp-dir=DIR create temporary files in directory DIR -y, --fuzzy find similar file for basis if no dest file --compare-dest=DIR also compare destination files relative to DIR --copy-dest=DIR ... and include copies of unchanged files --link-dest=DIR hardlink to files in DIR when unchanged -z, --compress compress file data during the transfer --compress-level=NUM explicitly set compression level --skip-compress=LIST skip compressing files with a suffix in LIST -C, --cvs-exclude auto-ignore files the same way CVS does -f, --filter=RULE add a file-filtering RULE -F same as --filter='dir-merge /.rsync-filter' repeated: --filter='- .rsync-filter' --exclude=PATTERN exclude files matching PATTERN --exclude-from=FILE read exclude patterns from FILE --include=PATTERN don't exclude files matching PATTERN --include-from=FILE read include patterns from FILE --files-from=FILE read list of source-file names from FILE -0, --from0 all *-from/filter files are delimited by 0s -s, --protect-args no space-splitting; only wildcard special-chars --address=ADDRESS bind address for outgoing socket to daemon --port=PORT specify double-colon alternate port number --sockopts=OPTIONS specify custom TCP options --blocking-io use blocking I/O for the remote shell --stats give some file-transfer stats -8, --8-bit-output leave high-bit chars unescaped in output -h, --human-readable output numbers in a human-readable format --progress show progress during transfer -P same as --partial --progress -i, --itemize-changes output a change-summary for all updates --out-format=FORMAT output updates using the specified FORMAT --log-file=FILE log what we're doing to the specified FILE --log-file-format=FMT log updates using the specified FMT --password-file=FILE read daemon-access password from FILE --list-only list the files instead of copying them --bwlimit=RATE limit socket I/O bandwidth --outbuf=N|L|B set output buffering to None, Line, or Block --write-batch=FILE write a batched update to FILE --only-write-batch=FILE like --write-batch but w/o updating destination --read-batch=FILE read a batched update from FILE --protocol=NUM force an older protocol version to be used --iconv=CONVERT_SPEC request charset conversion of filenames --checksum-seed=NUM set block/file checksum seed (advanced) -4, --ipv4 prefer IPv4 -6, --ipv6 prefer IPv6 --version print version number(-h) --help show this help (-h is --help only if used alone)Use "rsync --daemon --help" to see the daemon-mode command-line options.Please see the rsync(1) and rsyncd.conf(5) man pages for full documentation.See http://rsync.samba.org/ for updates, bug reports, and answers |
其中:
- -P same as –partial –progress
- –partial keep partially transferred files
- –progress show progress during transfer
- -a, –archive archive mode; equals -rlptgoD (no -H,-A,-X)
- -v, –verbose increase verbosity
- -z, –compress compress file data during the transfer
- -r, –recursive recurse into directories
- -e, –rsh=COMMAND specify the remote shell to use
另外对于:
1 | ssh -o 'ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:1080 %h %p' -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -o ServerAliveCountMax=20 |
再去看看ssh的参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | ssh --help ssh: illegal option -- -usage: ssh [-46AaCfGgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-B bind_interface] [-b bind_address] [-c cipher_spec] [-D [bind_address:]port] [-E log_file] [-e escape_char] [-F configfile] [-I pkcs11] [-i identity_file] [-J [user@]host[:port]] [-L address] [-l login_name] [-m mac_spec] [-O ctl_cmd] [-o option] [-p port] [-Q query_option] [-R address] [-S ctl_path] [-W host:port] [-w local_tun[:remote_tun]] destination [command] |
不清楚其中参数option含义
所以再去找找
man ssh
- -o option
- Can be used to give options in the format used in the configuration file. This is useful for specifying options for which there is no separate command-line flag. For full details of the options listed below, and their possible values, see ssh_config(5).
- AddressFamily
- BatchMode
- BindAddress
- ChallengeResponseAuthentication
- CheckHostIP
- Cipher
- Ciphers
- ClearAllForwardings
- Compression
- CompressionLevel
- ConnectionAttempts
- ConnectTimeout
- ControlMaster
- ControlPath
- DynamicForward
- EscapeChar
- ExitOnForwardFailure
- ForwardAgent
- ForwardX11
- ForwardX11Trusted
- GatewayPorts
- GlobalKnownHostsFile
- GSSAPIAuthentication
- GSSAPIDelegateCredentials
- HashKnownHosts
- Host’
- HostbasedAuthentication
- HostKeyAlgorithms
- HostKeyAlias
- HostName
- IdentityFile
- IdentitiesOnly
- KbdInteractiveDevices
- LocalCommand
- LocalForward
- LogLevel
- MACs’
- NoHostAuthenticationForLocalhost
- NumberOfPasswordPrompts
- PasswordAuthentication
- PermitLocalCommand
- Port’
- PreferredAuthentications
- Protocol
- ProxyCommand
- PubkeyAuthentication
- RekeyLimit
- RemoteForward
- RhostsRSAAuthentication
- RSAAuthentication
- SendEnv
- ServerAliveInterval
- ServerAliveCountMax
- SmartcardDevice
- StrictHostKeyChecking
- TCPKeepAlive
- Tunnel
- TunnelDevice
- UsePrivilegedPort
- User’
- UserKnownHostsFile
- VerifyHostKeyDNS
- VisualHostKey
- XAuthLocation
语法:
1 | nc [-46DdhklnrStUuvzC] [-i interval] [-p source_port] [-s source_ip_address] [-T ToS] [-w timeout] [-Xproxy_protocol] [-x proxy_address[:port]] [hostname] [port[s]] |
The nc (or netcat) utility is used for just about anything under the sun involving TCP or UDP. It can open TCP connections, send UDP packets, listen on arbitrary TCP and UDP ports, do port scanning, and deal with both IPv4 and IPv6. Unlike telnet(1), nc scripts nicely, and separates error messages onto standard error instead of sending them to standard output, as telnet(1) does with some.
- -X proxy_version
- Requests that nc should use the specified protocol when talking to the proxy server. Supported protocols are ”4” (SOCKS v.4), ”5” (SOCKS v.5) and ”connect” (HTTPS proxy). If the protocol is not specified, SOCKS version 5 is used.
- -x proxy_address[:port]
- Requests that nc should connect to hostname using a proxy at proxy_address and port. If port is not specified, the well-known port for the proxy protocol is used (1080 for SOCKS, 3128 for HTTPS).
-》看来此处的:
1 | nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:1080 %h %p |
含义是:
- -X 5
- SOCKS 5版协议
- 此处用的是SOCKS5代理(不是http代理)
- -x 127.0.0.1:1080
- 代理地址和端口是:127.0.0.1:1080
- %h %p
- 应该是对应着:[hostname] [port[s]]
- 分别表示:
- %host:当前主机 ?
- %p:当前端口 ?
另外的ssh的-o 表示option中的:
- ServerAliveInterval=30
- ServerAliveCountMax=20
成套工具:
- ssh(1) — The basic rlogin/rsh-like client program
- sshd(8) — The daemon that permits you to log in
- ssh_config(5) — The client configuration file
- sshd_config(5) — The daemon configuration file
- ssh-agent(1) — An authentication agent that can store private keys
- ssh-add(1) — Tool which adds keys to in the above agent
- sftp(1) — FTP-like program that works over SSH1 and SSH2 protocol
- scp(1) — File copy program that acts like rcp
- ssh-keygen(1) — Key generation tool
- sftp-server(8) — SFTP server subsystem (started automatically by sshd)
- ssh-keyscan(1) — Utility for gathering public host keys from a number of hosts
- ssh-keysign(8) — Helper program for host-based authentication
- ServerAliveInterval
- Sets a timeout interval in seconds after which if no data has been received from the server, ssh(1) will send a message through the encrypted channel to request a response from the server. The default is 0, indicating that these messages will not be sent to the server.
- ServerAliveCountMax
- Sets the number of server alive messages (see below) which may be sent without ssh(1) receiving any messages back from the server. If this threshold is reached while server alive messages are being sent, ssh will disconnect from the server, terminating the session. It is important to note that the use of server alive messages is very different from TCPKeepAlive(below). The server alive messages are sent through the encrypted channel and therefore will not be spoofable. The TCP keepalive option enabled by TCPKeepAlive is spoofable. The server alive mechanism is valuable when the client or server depend on knowing when a connection has become unresponsive.
- The default value is 3. If, for example, ServerAliveInterval (see below) is set to 15 and ServerAliveCountMax is left at the default, if the server becomes unresponsive, ssh will disconnect after approximately 45 seconds.
-》看起来,ServerAliveCountMax不应该次数太多
所以可以改为:
- ServerAliveInterval=30
- 每次最多30秒
- ServerAliveCountMax=5
- 最多5次
否则就(认为无响应)而和服务器断开
此处代理信息是:
1 | export HTTP_PROXY=http://127.0.0.1:58591; export HTTPS_PROXY=http://127.0.0.1:58591; export ALL_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:51837 |
所以可以去试试了
1 | ssh -o 'ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:51837 %h %p' -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -o ServerAliveCountMax=5 |
-》
1 | sshpass -f /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/common/config/deploy/deploy_server_password.txt rsync -avzh --progress --stats --delete --force -e "ssh -o 'ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:51837 %h %p' -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -o ServerAliveCountMax=5" /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/generated/books/android_app_security_crack/release/android_app_security_crack root@149.28.136.189:/data/wwwroot/book.crifan.com/books |
然后效果不错,加了代理后,速度还是挺快的:
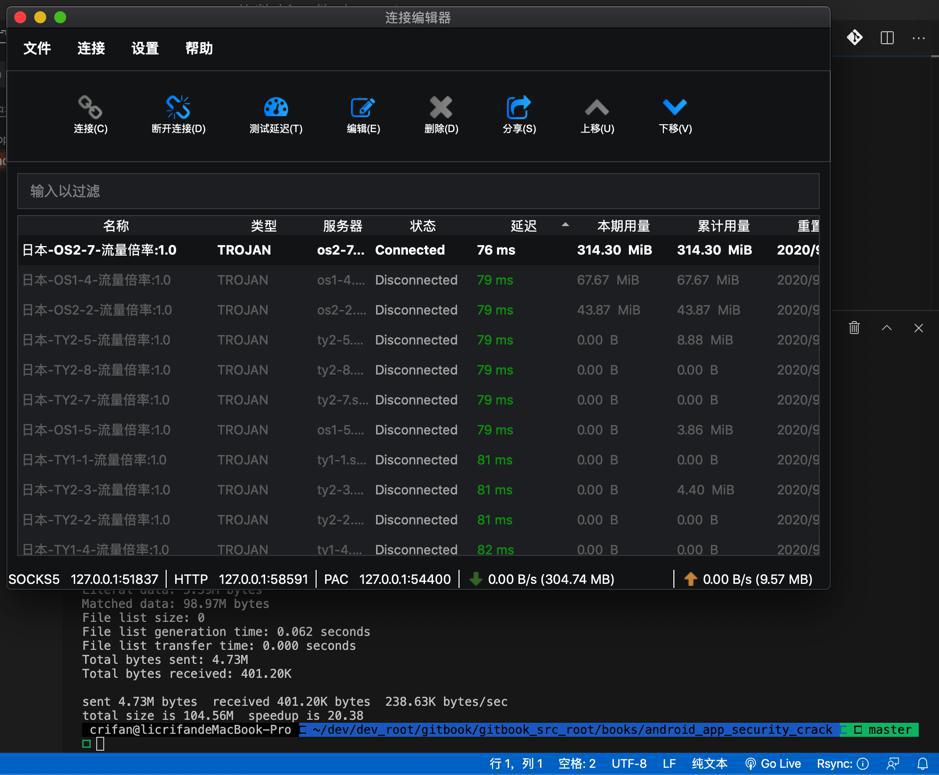
然后再把上述代理配置,加到makefile中
/Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/common/gitbook_makefile.mk
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | PROXY_SOCK5 = 127.0.0.1:51837# for rsync use sock5 proxyRSYNC_PROXY = -e "ssh -o 'ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x $(PROXY_SOCK5) %h %p' -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -o ServerAliveCountMax=5"# for rsync not use any proxy# RSYNC_PROXY = RSYNC_PARAMS = $(RSYNC_PROXY) -avzh --progress --stats --delete --force## Upload all genereted website/pdf/epub/mobi files to remote server using rsync. Create deploy_server_info.mk and deploy_server_password.txt which contain deploy server IP+User+Path and Password before use thisupload: all @echo ================================================================================ifeq ($(SHOULD_IGNORE), true) @echo Ignore upload $(BOOK_NAME) to book.crifan.comelse @echo Upload for $(BOOK_NAME) sshpass -f $(DEPLOY_SERVER_PASSWORD_FILE) rsync $(RSYNC_PARAMS) $(RELEASE_PATH) $(DEPLOY_SERVER_USER)@$(DEPLOY_SERVER_IP):$(DEPLOY_SERVER_PATH)endif...## Commit generated files to github iocommit: all @echo ================================================================================ @echo Commit for $(BOOK_NAME) rsync $(RSYNC_PARAMS) $(RELEASE_PATH) $(GITHUB_IO_PATH)... |
去试了试,是可以的。
如果后续不想用代理,则可以直接开启上述的:
1 | RSYNC_PROXY = |
即可。
【总结】
此处,可以通过给rsync加代理,实现加快文件同步上传的速度。
具体方式是:
之前是:
1 | sshpass -f /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/common/config/deploy/deploy_server_password.txt rsync -avzh --progress --stats --delete --force /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/generated/books/android_app_security_crack/release/android_app_security_crack root@149.28.136.189:/data/wwwroot/book.crifan.com/books |
现在是:
1 | sshpass -f /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/common/config/deploy/deploy_server_password.txt rsync -avzh --progress --stats --delete --force -e "ssh -o 'ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:51837 %h %p' -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -o ServerAliveCountMax=5" /Users/crifan/dev/dev_root/gitbook/gitbook_src_root/generated/books/android_app_security_crack/release/android_app_security_crack root@149.28.136.189:/data/wwwroot/book.crifan.com/books |
即可。
其中参数含义解释:
- rsync
- -e, –rsh=COMMAND specify the remote shell to use
- ssh -o ‘ProxyCommand nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:51837 %h %p’ -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -o ServerAliveCountMax=5
- ssh
- -o option
- Can be used to give options in the format used in the configuration file. This is useful for specifying options for which there is no separate command-line flag. For full details of the options listed below, and their possible values
- ProxyCommand
- nc -X 5 -x 127.0.0.1:51837 %h %p
- 参数语法
- -X proxy_version
- Requests that nc should use the specified protocol when talking to the proxy server. Supported protocols are ”4” (SOCKS v.4), ”5” (SOCKS v.5) and ”connect” (HTTPS proxy). If the protocol is not specified, SOCKS version 5 is used.
- -x proxy_address[:port]
- Requests that nc should connect to hostname using a proxy at proxy_address and port. If port is not specified, the well-known port for the proxy protocol is used (1080 for SOCKS, 3128 for HTTPS).
- 参数含义
- -X 5
- SOCKS 5版协议
- 此处用的是SOCKS5代理(不是http代理)
- -x 127.0.0.1:1080
- 代理地址和端口是:127.0.0.1:1080
- %h %p
- 应该是对应着:[hostname] [port[s]]
- 分别表示:
- %host:当前主机 ?
- %p:当前端口 ?
- ssh_config
- 参数语法
- ServerAliveInterval
- Sets a timeout interval in seconds after which if no data has been received from the server, ssh(1) will send a message through the encrypted channel to request a response from the server. The default is 0, indicating that these messages will not be sent to the server.
- ServerAliveCountMax
- Sets the number of server alive messages (see below) which may be sent without ssh(1) receiving any messages back from the server. If this threshold is reached while server alive messages are being sent, ssh will disconnect from the server, terminating the session. It is important to note that the use of server alive messages is very different from TCPKeepAlive(below). The server alive messages are sent through the encrypted channel and therefore will not be spoofable. The TCP keepalive option enabled by TCPKeepAlive is spoofable. The server alive mechanism is valuable when the client or server depend on knowing when a connection has become unresponsive.
- The default value is 3. If, for example, ServerAliveInterval (see below) is set to 15 and ServerAliveCountMax is left at the default, if the server becomes unresponsive, ssh will disconnect after approximately 45 seconds.
- 参数含义
- ServerAliveInterval=30
- 每次最多30秒
- ServerAliveCountMax=5
- 最多5次
转载请注明:在路上 » 【已解决】给用sshpass的rsync加代理以加速