已经实现了基本的:
但是此处程序是各种复杂的视图,所以要去研究复杂的视图如何实现:
iOS swift 恢复程序状态
Swift App状态恢复-State Restoration(一) – Wenchen的专栏 – 博客频道 – CSDN.NET
iOS开发那些事–iOS6 UI状态保持和恢复 – 关东升 – 博客频道 – CSDN.NET
ios 状态恢复 vs 持久化存储
ios state preservation vs persistent
ios 状态保存和恢复
备忘录模式 – Memento – iOS 中的设计模式 (Swift版本) – 极客学院Wiki
State Preservation and Restoration – Use Your Loaf
Restoration Classes and UIWebViews – Use Your Loaf
An Overview of iOS 7 Application State Preservation and Restoration – Techotopia
An iOS 7 State Preservation and Restoration Tutorial – Techotopia
抽空去搞清楚:
设置视图控制器的restorationIdentifier,放在哪个位置去初始化比较合适:
init还是viewDidLoad?
UIDataSourceModelAssociation Protocol Reference
[总结]
首先:
app(用户主动或被系统被动)关掉后再打开,还是之前的样子
叫做:State Preservation and Restoration,状态的保存和恢复
保存和恢复的关键点在于:app的进入后台background
(iOS模拟器中可以通过-》模拟器-》主界面而回到主界面去触发此保存的机制)
此时UIKit通过:
-》AppDelegate中的shouldSaveApplicationState
-》从视图view的层次hierarchy中,以此决定,哪个,哪些视图View和视图控制器ViewController需要备份
-》给那些restorationIdentifier不为空的view去备份
-》然后UIKit就以此调用对应的View或ViewController中的encodeRestorableStateWithCoder去保存备份你的当天的状态数据
-》具体要保存哪些数据,是你自己负责的
-》往往都是你自己的View或ViewController中的类的各种字视图subview和其它一些变量,数据等内容
-》encodeRestorableStateWithCoder中会调用coder.encodeObject之类的函数,底层实现,则是调用到对应的此处的Object所对应的变量中的encodeWithCoder去完成真正的数据保存的工作的
-》对应的要保存的数据的变量或类,都要支持:
继承了NSObject和NSCoding
且实现了func encodeWithCoder(aCoder: NSCoder)
-》程序状态数据都保存完毕后,此时:
程序如果被系统关闭掉了
(可以通过Xcode中,点击Stop停止键去模拟此程序被关闭的情况)
-》然后再次打开被中断掉的程序
(不要在Xcode中点击Run运行-》该Run会导致重新安装程序-》而把之前的程序覆盖掉-》无法实现模拟重新打开被关闭了的程序的效果了)
(可以通过:鼠标点击被关闭了的,iOS模拟器中的程序,即可打开)
-》然后就进入了恢复的过程:
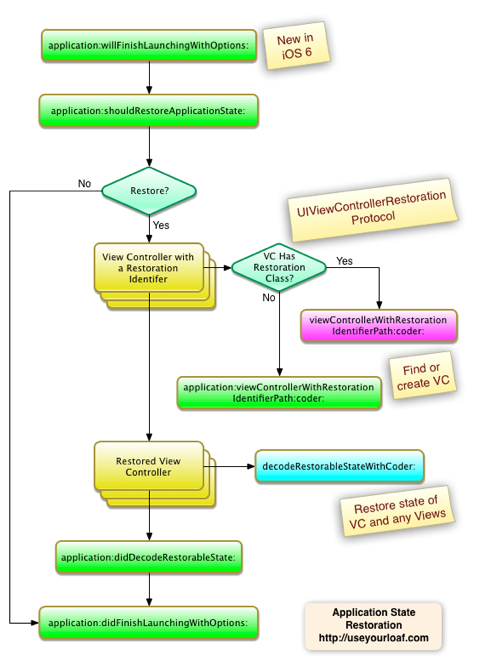
-》调用AppDelegate中的willFinishLaunchingWithOptions
-》shouldRestoreApplicationState
-》然后去挨个恢复,带有恢复标识符的视图控制器(View Controller with restoration identifier)
(对应的就是你的对应的代码:
self.restorationIdentifier = String(self.dynamicType) |
去设置了restorationIdentifier
-》对于每个要恢复的类class,再去判断是否有对应的恢复类Restoration Class
(对应的就是你的代码中的类似于这样的代码:
self.restorationClass = self.dynamicType //only for view controller need this |
去设置的restorationClass)
-》不论是:
restorationIdentifier
还是:
restorationClass
都是对应的UIStateRestoring协议规定的,而UIViewController实现了此UIStateRestoring:
UIViewController.swift
extension UIViewController : UIStateRestoring { @available(iOS 6.0, *) public var restorationIdentifier: String? @available(iOS 6.0, *) public var restorationClass: AnyObject.Type? @available(iOS 6.0, *) public func encodeRestorableStateWithCoder(coder: NSCoder) @available(iOS 6.0, *) public func decodeRestorableStateWithCoder(coder: NSCoder) @available(iOS 7.0, *) public func applicationFinishedRestoringState() } |
-》如果视图控制器中有了此Restoration Class,则调用该视图控制器中的
func viewControllerWithRestorationIdentifierPath(identifierComponents: [AnyObject], coder: NSCoder) -> UIViewController? { |
如果VC中没有,则去调用application中的:
func application(application: UIApplication, viewControllerWithRestorationIdentifierPath identifierComponents: [AnyObject], coder: NSCoder) -> UIViewController? |
-》此处,不论是VC自己的viewControllerWithRestorationIdentifierPath还是application的viewControllerWithRestorationIdentifierPath,注意到都是返回了UIViewController,返回了对应的VC实例
-》接下来,才是调用viewControllerWithRestorationIdentifierPath得到的VC实例的decodeRestorableStateWithCoder去恢复之前保存的数据
注意:
在恢复出来数据之后,往往还要加上一些你自己的合适的代码,确保你的UI界面正常显示内容了
比如:把恢复出来的text设置给对应的textFiled的text
把恢复出来的tableView的data对应的tableview去reloadData以便于刷新数据,确保界面显示正常等等。
-》最后才是调用application的
func application(application: UIApplication, didDecodeRestorableStateWithCoder coder: NSCoder) |
程序数据模型 和 图形界面状态 是不一样的。
而此处的状态保存和恢复,主要针对于的是用户状态
-》如果用户主动强制退出程序的话,则之前保存的状态数据,则会被删除掉。
-》所以最好不要用此状态保存和恢复的机制,去保存应用程序数据模型
-》应用程序数据最好保存到持久性存储:写入到文件,数据库,CoreData
-》
application:willFinishLaunchingWithOptions
application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions
中的willFinishLaunchingWithOptions
是在状态恢复之前执行的
-》所以数据模型相关的动作和初始化,应该放在willFinishLaunchingWithOptions
-》这样开始状态恢复的时候,对于的数据就已经准备好了,对应的状态才能正常的被恢复
转载请注明:在路上 » [整理]swift iOS程序状态保存和恢复